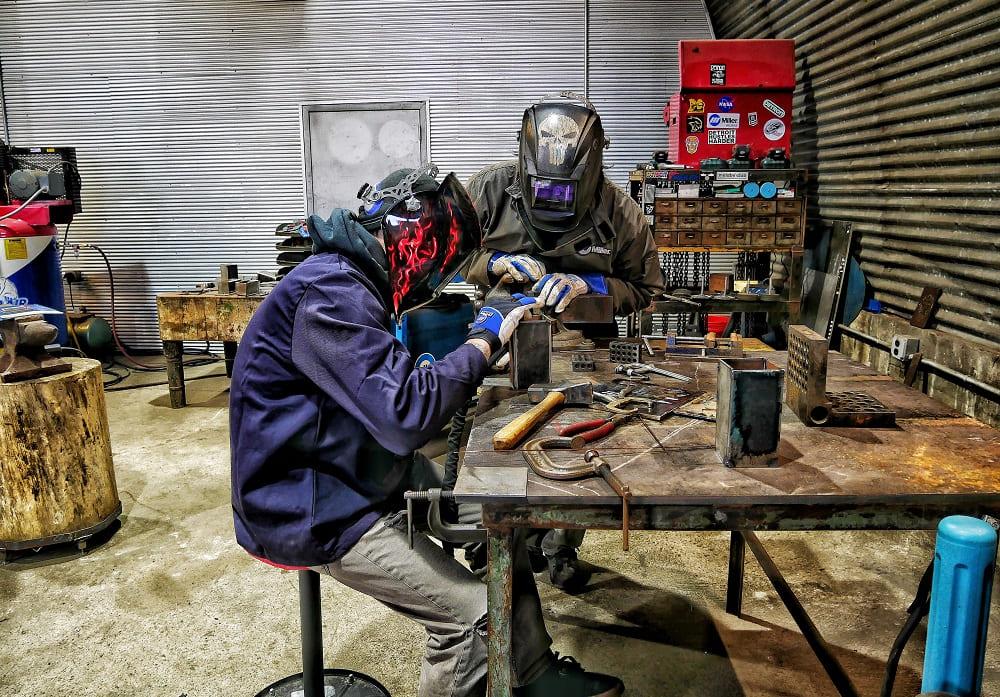
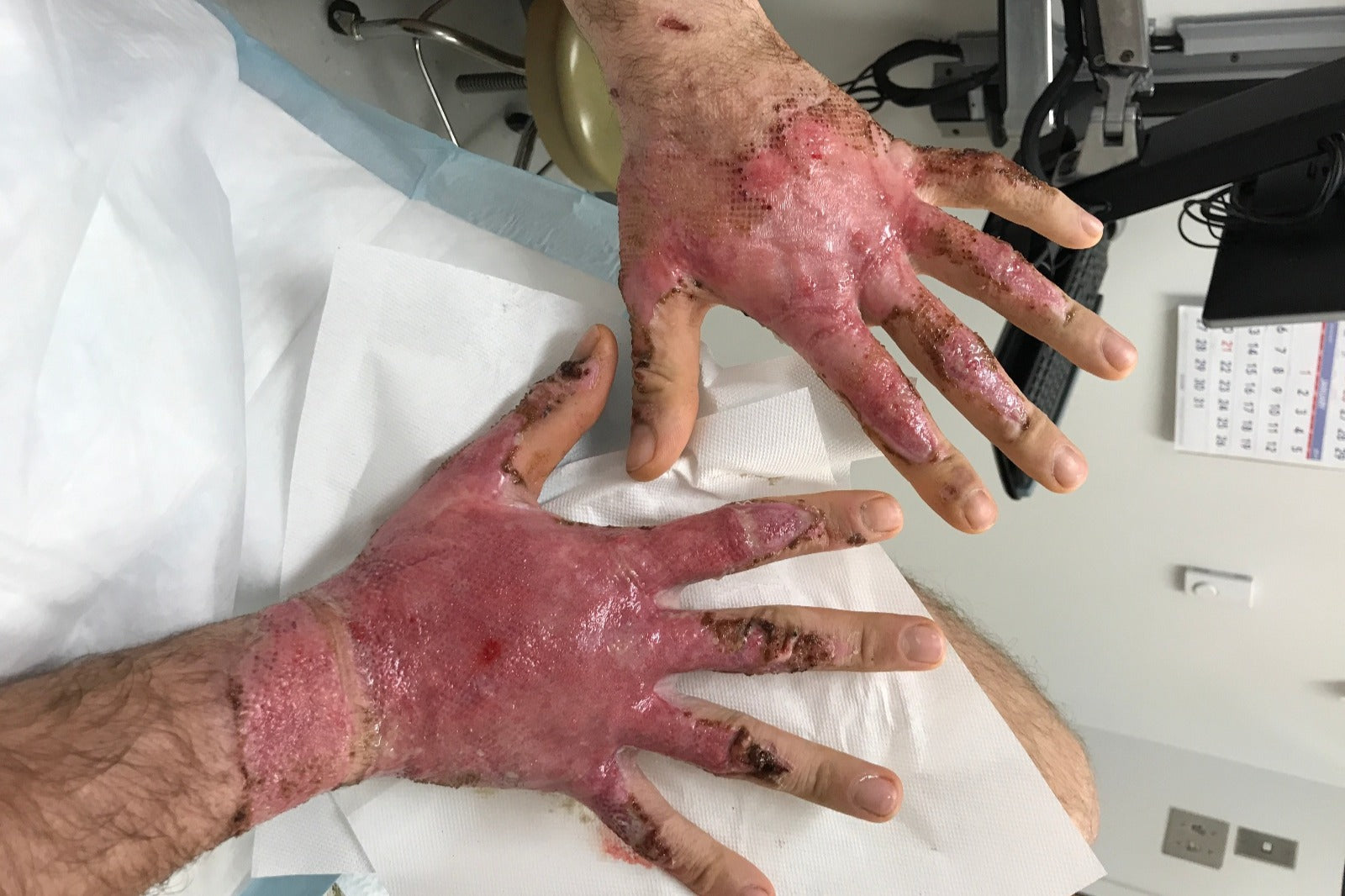
In the dynamic world of industrial work, few occupations carry as much inherent risk as welding. Beyond the obvious dangers of heat and fumes, one of the most common and often underestimated hazards faced by welders is burns. These injuries can range from minor discomfort to severe, life-altering wounds, making understanding their prevalence and prevention critical for both employers and workers alike.
Understanding the Risk: Welding involves the use of high temperatures to fuse metals together, generating intense heat and sparks. This environment exposes welders to several types of burns:
- Thermal Burns: Direct contact with hot metal, molten slag, or welding arcs can cause thermal burns, which vary in severity depending on exposure time and the temperature of the material.
-
Arc Burns: Exposure to the ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation emitted during welding can lead to arc burns, also known as flash burns or "welder's flash." These burns affect the eyes and skin and are akin to severe sunburns.
-
Chemical Burns: Some welding processes involve the use of chemicals like fluxes and cleaning agents, which can cause chemical burns if they come into contact with the skin.
The Scope of the Issue: Burns are among the most commonly reported injuries in the welding industry. According to data from occupational health and safety agencies and industry reports:
-
Prevalence: Burns account for a significant portion of welding-related injuries. In some studies, they constitute up to 20% of reported incidents, highlighting their frequent occurrence.
-
Severity: While many burns are minor and can be treated on-site or with basic first aid, severe burns requiring hospitalization are not uncommon. These injuries can result in long-term medical issues and significant downtime for affected workers.
Factors Contributing to Burns: Several factors contribute to the frequency of burns in welding:
-
Lack of Proper PPE: Inadequate or improper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, welding helmets with appropriate lenses, and fire-resistant clothing, increases the risk of burns.
-
Human Error: Even experienced welders can be vulnerable to accidents due to lapses in concentration, fatigue, or complacency.
-
Environmental Conditions: Tight spaces, awkward postures, and confined work areas can exacerbate the risk of accidental contact with hot surfaces or materials.
Prevention Strategies: Efforts to reduce the incidence of burns in the welding industry focus on a combination of training, engineering controls, and administrative measures:
-
Training and Education: Proper training on the use of PPE, safe welding techniques, and recognizing the signs of potential burns are crucial.
-
Engineering Controls: Implementing measures such as local exhaust ventilation systems to remove welding fumes and using automated welding equipment can minimize direct exposure to heat and radiation.
-
Administrative Controls: Rotating workers to minimize exposure time, conducting regular hazard assessments, and enforcing strict safety protocols contribute to a safer working environment.
Burn Treatment: Treating welding burns promptly and correctly is crucial to minimize pain, prevent infection, and promote healing. Here are the steps typically recommended for treating welding burns:
1. Assess the Severity
- Minor Burns: These affect only the outer layer of skin (epidermis) and cause redness and pain.
- Moderate Burns: These penetrate deeper into the skin layers (dermis) and may cause blisters, swelling, and intense pain.
- Severe Burns: These extend through all skin layers and may involve underlying tissues, causing charred or white skin, numbness, and potentially severe pain.
2. Immediate First Aid
- Stop the Burning Process: Remove the heat source or the affected person from the source of the burn.
- Cool the Burn: Hold the burned area under cool (not cold) running water for at least 10-20 minutes. This helps reduce pain, swelling, and further damage to the tissue. Do not use ice or very cold water as it can worsen tissue damage.
- Remove Constricting Items: If the burn is on an extremity, remove jewelry, watches, or tight clothing around the burned area before swelling occurs.
3. Assess for Blisters and Debris
- Do Not Pop Blisters: Blisters can protect the underlying skin from infection. Popping them increases the risk of infection.
- Remove Debris: If there are loose particles or dirt on the burn, gently remove them with clean, sterile tweezers or gauze.
4. Apply a Burn Dressing
- Use a Non-Adhesive Dressing: Apply a non-stick sterile dressing or a clean, dry cloth to cover the burn. Avoid using adhesive dressings as they can stick to the burn and cause more damage when removed.
- Loosely Wrap: If needed, loosely wrap the dressing around the burn to protect it from friction and contamination.
5. Pain Management
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: If pain is significant, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be taken according to package instructions. Avoid aspirin in adults and children under 16 due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.
6. Seek Medical Attention
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Depending on the severity of the burn, seek medical attention promptly. This is especially important for moderate to severe burns, burns on the face, hands, feet, or genitals, or burns that cover a large area of the body.
7. Prevent Infection and Promote Healing
- Keep the Burn Clean: Wash the burn gently with mild soap and water daily, and pat it dry with a clean cloth or gauze.
- Apply Antibiotic Ointment: If advised by a healthcare professional, apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment to the burn before reapplying a clean dressing.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Watch for increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth around the burn, or pus drainage, which may indicate infection.
8. Follow-up Care
- Attend Follow-up Appointments: If prescribed by a healthcare professional, attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress and ensure proper wound care.
Important Considerations
- Do Not Use Home Remedies: Avoid applying butter, oils, ice, or toothpaste to burns, as these can worsen the injury and increase the risk of infection.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, which supports overall healing.
By following these steps promptly and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can effectively manage welding burns, reduce complications, and promote a quicker recovery.
Conclusion: Burns remain a significant occupational hazard in the welding industry, impacting the health, safety, and productivity of workers. While advances in technology and safety practices have mitigated some risks, vigilance and adherence to safety protocols are essential to further reduce the incidence of these injuries. Employers and workers must continue to prioritize safety through ongoing education, appropriate use of protective gear, and a commitment to fostering a culture of safety in the workplace. By doing so, the welding industry can work towards minimizing the frequency and severity of burns, ensuring a safer and more secure environment for all involved.